Embracing Neurodiversity: Universal and Inclusive Design in Virtual Reality Experiences
- Jeff Rayner

- Jun 13, 2023
- 3 min read
Introduction: Virtual Reality (VR) has emerged as a powerful tool in education, entertainment, and various other industries. Its immersive nature enables users to explore new worlds, gain new perspectives, and engage with content in unprecedented ways. However, to ensure equal access and participation for all individuals, it is crucial to integrate universal and inclusive design principles into VR experiences. This article explores the groundbreaking uniVRsal project, a collaboration between TERC and MXTreality, which aims to create inclusive VR experiences specifically designed for neurodiverse learners.

Understanding Neurodiversity: Neurodiversity is a concept that recognizes and celebrates the natural variations in the human brain and the diversity of neurological conditions such as autism, ADHD, dyslexia, and more. It emphasizes that these differences are simply part of the natural spectrum of human abilities, rather than something to be fixed or normalized.
Challenges Faced by Neurodiverse Learners: Neurodiverse learners often encounter unique challenges in traditional educational settings. They may struggle with sensory overload, social interactions, information processing, and attention-related difficulties. VR, with its ability to create controlled and customizable environments, offers a promising solution to address these challenges.
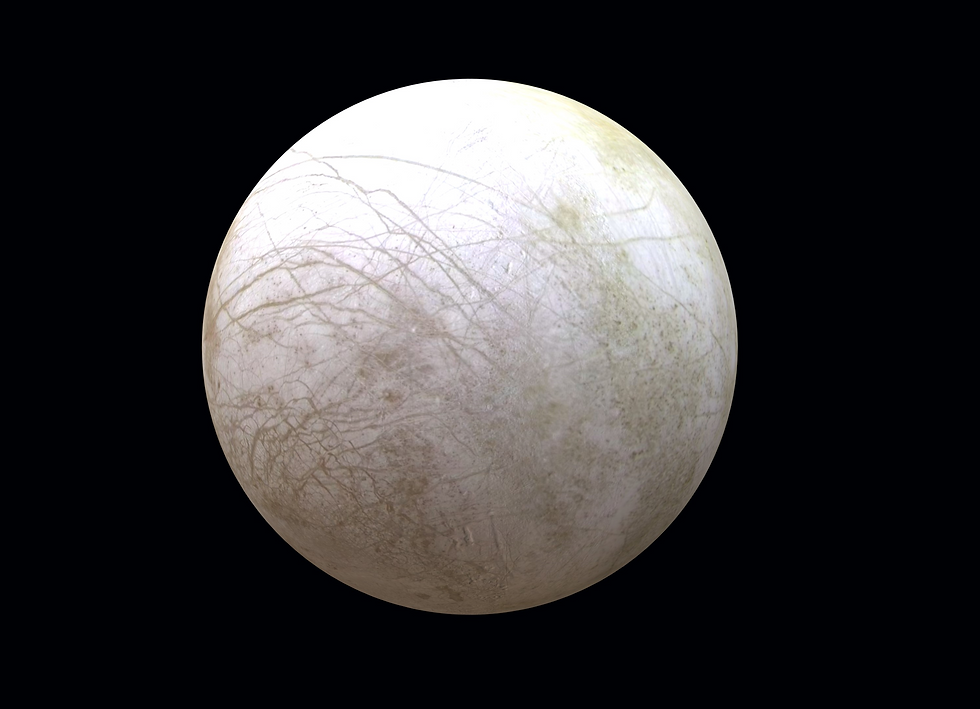
The uniVRsal Project: The uniVRsal project is a pioneering initiative that seeks to develop inclusive and adaptive VR experiences tailored to the specific needs of neurodiverse learners. It is a collaborative effort developed for and with EdGE at TERC, terc.edu/edge, as part of an NSF-funded project (#2005447) to research and develop a STEM-based VR game for a broad audience, including neurodivergent players. This Europa based virtual puzzle solving adventure aims to broaden participation in informal STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, Math) learning for all, yet with a special focus on neuro-diverse and autistic learners through the magic offered via virtual reality.
Key Principles of Universal and Inclusive Design in VR:
Accessibility: Designing VR experiences that are accessible to individuals with diverse abilities, including those with sensory, cognitive, or motor impairments. This may involve providing adjustable settings for audio, visual, and haptic feedback, as well as customizable controls and interfaces.
Personalization: Allowing users to personalize their VR experiences to accommodate their specific needs. This includes options to modify the pace, difficulty level, or visual representations of content, catering to individual preferences and learning styles.
Multimodal Feedback: Incorporating multiple sensory modalities, such as visual, auditory, and tactile feedback, to enhance learning and engagement. Utilizing a combination of text, audio, and visual cues ensures that learners can process information through their preferred channels.
Clear Instructions and Guidance: Providing clear instructions and intuitive guidance within the VR environment to minimize confusion and frustration. This can involve visual cues, interactive tutorials, or voice prompts that guide learners through tasks and activities.
Collaboration and Social Interaction: Encouraging collaborative experiences and social interactions within the VR environment. This helps neurodiverse learners develop essential social skills in a safe and controlled setting, fostering inclusivity and understanding.
Benefits of uniVRsal for Neurodiverse Learners: The uniVRsal project holds immense potential for neurodiverse learners, offering a range of benefits:
Tailored Learning Environments: VR enables the creation of customizable and immersive learning environments that cater to individual strengths and needs. Learners can engage with content at their own pace, facilitating personalized and meaningful learning experiences.
Sensory Integration: By providing controlled sensory stimuli, VR can help neurodiverse learners develop sensory integration skills. They can gradually acclimate to sensory inputs and build tolerance in a safe and supportive environment.
Empathy and Perspective-Taking: VR experiences can foster empathy and understanding by enabling learners to see the world through different perspectives. This can contribute to greater acceptance and appreciation of neurodiversity among learners and society as a whole.
Real-World Simulations: VR allows for realistic and immersive simulations that facilitate skill development in a safe and repeatable manner. Neurodiverse learners can practice social interactions, problem-solving, and other essential skills in a controlled environment before applying them in real-world scenarios.
Conclusion: The integration of universal and inclusive design principles in VR experiences, as exemplified by the uniVRsal project, holds tremendous promise for neurodiverse learners. By recognizing and embracing neurodiversity, we can create VR environments that empower individuals to learn, grow, and thrive in ways that suit their unique abilities and needs. The uniVRsal project stands as a testament to the transformative power of VR, paving the way for a more inclusive and equitable future for all learners.
More Info: Developed by MXTreality for and with EdGE at TERC, terc.edu/edge, as part of an NSF-funded project (#2005447) researching and developing a STEM-based VR game for a broad audience, including neurodivergent players. This collaboration between MXTreality & TERC aims to broaden participation in informal STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, Math) learning for all, yet with a special focus on neuro-diverse and autistic learners through the magic offered via virtual reality.
NSF Grant: DRL-2005447 #uniVRsal #EuropaPrime #TERC #MXTreality #neurodiverse #neurodiversity #NSF #Jupiter #Minos #FlameJelly #Space
For more information, please see https://www.terc.edu/projects/univrsa... https://www.mxtreality.com/europa






Comments